Learn How to Store Solar Energy and Future-Proof Your Home
Updated: 04 Dec 2024
87
Introduction
Solar energy is one of the most abundant sources of power on Earth, but it has a major limitation: it’s only available when the sun is shining. With the growing need for clean, renewable energy, figuring out how to store solar energy efficiently is becoming more important than ever. Without proper storage, solar power can’t be used when needed most.
Fortunately, there are solutions. Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and other systems, allow us to capture solar energy and use it at any time whether it’s a cloudy day or night.
How Solar Energy is Stored
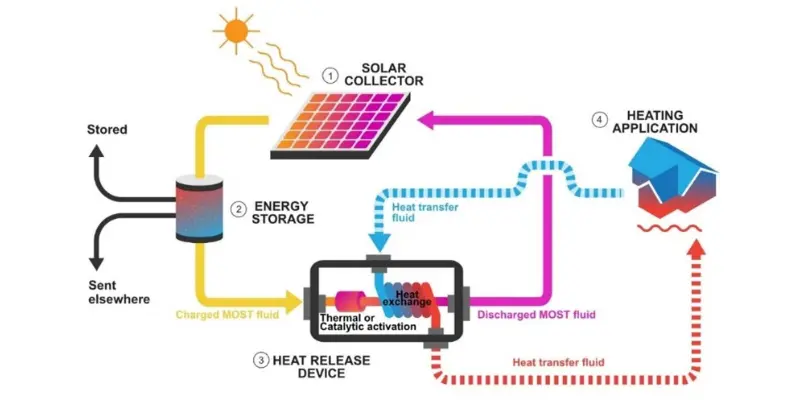
Battery Storage
- What it is: Solar energy is stored in batteries for later use, especially when the sun isn’t shining. These batteries store the energy produced by solar panels as chemical energy, which can later be converted back to electricity.
- Types of Batteries: The most common types of batteries used for solar storage are lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries, and nickel-cadmium batteries. Each has its own advantages depending on cost, efficiency, and lifespan.
Example: A typical home battery storage system consists of lithium-ion batteries, like those in the Tesla Powerwall, which stores excess solar energy produced during the day and releases it at night or during cloudy periods.
How Does Solar Energy Storage Work?
Step 1: Energy Collection
- Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through photovoltaic cells. This electricity is in direct current (DC) form.
- Tip: Before energy can be stored, a solar panel system must first collect enough sunlight.
Step 2: Storing the Energy
- The electricity is then directed to a storage system such as batteries or thermal units.
- Example: A solar inverter ensures that power is safely directed into storage while managing the flow of electricity.
Step 3: Using Stored Energy
- When the sun isn’t shining (e.g., at night or on cloudy days), the stored energy is used to power your home or business.
- Tip: Inverters convert the DC electricity from batteries to AC power, which is used by most home appliances.
Benefits of Storing Solar Energy

Balancing Supply and Demand
- Storage helps balance power generation and consumption, especially during peak demand hours when solar production may be low.
- Example: Excess solar power collected during the day can be stored and used in the evening when electricity demand is highest.
Cost Savings
- Storing solar energy reduces electricity bills by using self-generated power instead of relying on grid electricity.
- Example: Battery storage systems can be particularly useful for time-of-use (TOU) billing, helping homeowners avoid peak-hour electricity rates.
Energy Resilience and Backup
- Solar storage systems provide backup power during outages, ensuring continued access to electricity.
- Tip: For homeowners in areas prone to natural disasters or power grid instability, solar storage is crucial for maintaining energy access during emergencies.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
- Using stored solar energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Example: When solar power replaces grid electricity, it helps reduce carbon emissions, making homes more eco-friendly and sustainable.
Types of Solar Energy Storage Systems
Residential Storage
- For homeowners, residential solar energy storage typically involves lithium-ion batteries, which store excess energy generated by solar panels for later use.
- Example: The Tesla Powerwall is a popular option for residential solar storage. It stores solar energy during the day and supplies power during the night or during power outages, helping homeowners save on energy bills and provide backup power.
Commercial and Utility Storage
- Businesses and utility providers require larger storage systems to manage significant energy needs. These systems are designed to store large amounts of solar energy for high-demand periods and provide grid support.
- Example: Pumped hydro storage and large-scale lithium-ion battery banks are commonly used by utilities. For instance, California’s large solar power plants often pair with utility-scale storage systems to balance supply and demand, especially during peak hours or at night.
Cost Considerations
- The cost of solar energy storage varies depending on the type and scale of the system. Residential storage systems can range from $5,000 to $15,000 for smaller setups, while commercial and utility-scale systems can cost millions.
- Tip: When choosing a solar storage system, consider your energy usage, available space, and budget. Residential systems may be sufficient for homes with moderate electricity use, while larger businesses or utilities may need more robust solutions to handle greater energy demands.
Challenges and Considerations
Storage Duration
- Different storage systems have varying durations for which they can store energy. For example, a typical battery system can store energy for 1-5 days, depending on capacity and usage.
- Tip: In areas with extended cloudy periods or limited sunlight, consider larger battery systems or hybrid storage solutions like combining batteries with thermal storage.
Initial Costs
- The initial investment for solar and storage systems can be significant, covering the cost of panels, inverters, and storage units.
- Example: A residential solar setup with battery storage might cost anywhere from $10,000 to $30,000, depending on the size and technology used.
Technology and Efficiency
- The efficiency of energy storage systems can vary. For example, lithium-ion batteries are more efficient but come with higher costs, while lead-acid batteries are more affordable but less efficient.
- Tip: Ongoing advancements in solar and storage technology are helping lower costs and improve performance, making them more accessible for homeowners and businesses alike.
| Advantages of Solar Energy Storage |
|---|
Energy Independence: Storing solar energy enables homeowners and businesses to reduce their reliance on grid power, providing energy security and peace of mind. Lower Electricity Bills: By using self-generated solar power stored in batteries, you can reduce electricity consumption from the grid, leading to significant cost savings, especially during peak hours. Backup Power During Outages: Solar energy storage systems provide backup power during grid outages, ensuring that essential devices and appliances continue to operate when the power goes out. Environmental Impact: Storing solar energy reduces the need for fossil fuel-based electricity, helping lower carbon emissions and contributing to a greener, more sustainable future. Increased Home Value: Homes equipped with solar and storage systems tend to have higher property values due to the long-term savings and energy independence they offer. Peak Demand Management: Stored solar energy helps balance supply and demand, particularly during peak electricity usage hours when solar energy production may be insufficient. Flexibility in Energy Usage: Solar energy storage allows users to consume stored energy whenever they need it, even when the sun isn’t shining, ensuring continuous power availability. Time-of-Use (TOU) Savings: With time-of-use billing, solar storage can help homeowners and businesses avoid high electricity costs during peak rate periods by using stored energy instead of drawing from the grid. Improved Grid Resilience: Solar storage contributes to a more resilient power grid by reducing strain during peak times and offering support in case of disruptions or emergencies. Technological Advancements: Ongoing advancements in solar and storage technologies are making energy storage systems more efficient, affordable, and accessible for consumers, increasing their attractiveness for both residential and commercial use. |
Conclusion
Solar energy storage, through methods like batteries and thermal systems, helps maximize energy use by storing excess power for later. With systems like lithium-ion batteries or pumped hydro, you can reduce costs, enhance energy reliability, and decrease your carbon footprint. Whether you need 5 kW for your home or 100+ kW for commercial use, solar storage offers a smart, sustainable solution. Consider installing a solar storage system today to optimize your energy usage and future-proof your power needs!
Can solar energy be stored for future use?
Yes, solar energy can be stored using various methods such as batteries, thermal storage (like molten salt), and mechanical storage (such as pumped hydro). These systems store excess solar energy for later use when sunlight is not available.
What is the most cost-effective way to store solar energy?
The cost-effectiveness of solar storage depends on factors like energy usage, location, and system size. Batteries (such as lithium-ion) are the most common for residential use, but thermal storage and mechanical systems like flywheels or pumped hydro are often more economical at a larger scale (e.g., for utilities).
How long do solar batteries last?
Most solar batteries, especially lithium-ion types, last between 15-30 years depending on usage and environmental conditions. Battery lifespan may vary based on the frequency of charge and discharge cycles.
Is solar storage worth the investment?
Whether solar storage is worth the investment depends on your location, electricity rates, and energy needs. It may be particularly beneficial for homeowners in areas with high electricity costs, frequent power outages, or a significant amount of sunlight throughout the year.
How much does solar battery storage cost?
The cost of solar battery storage can range from $5,000 to $15,000 for residential systems. Larger, utility-scale systems can be more expensive. The price varies depending on the battery capacity, brand, and installation fees.
Do solar batteries work in power outages?
Yes, many solar battery systems, like Tesla Powerwall, can provide backup power during outages. The stored energy is automatically used when the grid goes down, allowing you to keep essential appliances running.
Can I install solar storage with an existing solar system?
Yes, you can add solar storage to an existing solar setup. If your system is already generating energy but not storing it, adding a battery storage system is a straightforward way to store excess energy for later use.
How does solar storage help with peak electricity demand?
Solar storage helps by storing excess energy during the day when sunlight is abundant and electricity demand is lower. This stored energy can then be used during peak hours, such as in the evening when demand is high, reducing reliance on grid power.
Please Write Your Comments