What is TSRF Solar? A Complete Guide to Total Solar Resource Fraction
Updated: 20 Dec 2024
182

Introduction
TSRF Solar (Total Solar Resource Fraction) is a crucial metric used to assess the solar energy potential of any given location. By considering factors like shading, panel tilt, and orientation, TSRF Solar helps determine how much sunlight an area can capture throughout the year. Understanding TSRF Solar is essential for accurately predicting energy production and ensuring the most effective solar panel installation. Ready to optimize your solar system?
Explore more about TSRF Solar and make informed decisions for your energy future!
What is TSRF Solar? A Comprehensive Guide to Total Solar Resource Factor
TSRF (Total Solar Resource Fraction) is a key metric used in the solar industry to measure the solar energy potential of a specific location. This value helps determine the amount of sunlight a given area can capture over the year, accounting for the site’s unique conditions, such as shading, tilt, and orientation. Understanding TSRF is essential when assessing whether a site is suitable for solar energy generation.
Why TSRF is Important for Solar Energy
The Total Solar Resource Fraction (TSRF) plays a crucial role in designing solar energy systems. By evaluating the TSRF of a site, solar installers and engineers can predict how much energy a solar system can produce based on local conditions. This helps in making more accurate energy predictions, optimizing system performance, and ensuring that the solar panels are installed in the most effective manner.
- For example, a higher TSRF indicates that the site receives a lot of sunlight, and installing solar panels there will produce more energy. A lower TSRF may signal significant shading or poor orientation, reducing the efficiency of the system.
How Does TSRF Solar Work?
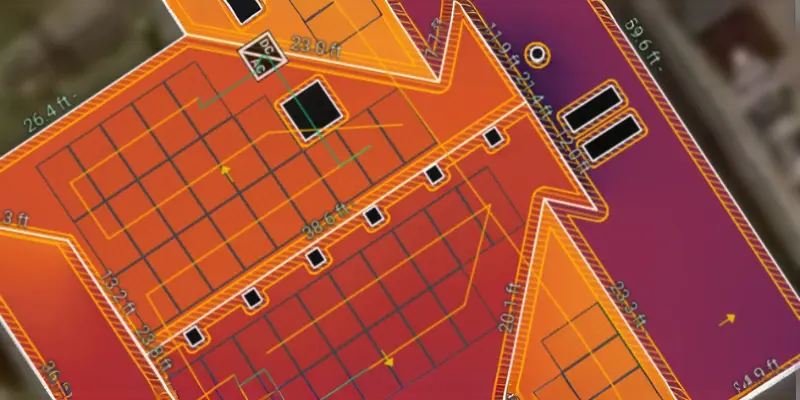
To calculate TSRF, a few factors are considered:
- Geographical Location: Locations closer to the equator receive more sunlight than those near the poles, making them ideal for solar energy.
- Orientation and Tilt of Panels: The angle at which solar panels are tilted and the direction they face will affect the amount of sunlight they receive. Panels facing south in the Northern Hemisphere typically get the most sunlight.
- Shading: Trees, buildings, or nearby hills can block sunlight, reducing the amount of energy solar panels can produce. This factor is critical when calculating TSRF.
- Atmospheric Conditions: Cloud cover, frequent rainfall, or snow can reduce solar exposure, which lowers the potential for solar energy generation.
- Solar Panel Efficiency: Different solar panel technologies have different efficiency levels, so the type of panel used plays a significant role in determining the TSRF.
Key Factors Influencing TSRF Solar
Several factors directly affect TSRF, and understanding them helps in accurately assessing the suitability of a site for solar energy production:
- Geographical Location: Areas closer to the equator receive more sunlight throughout the year, resulting in higher TSRF values.
- Orientation and Tilt of Panels: Solar panels that face the south (in the Northern Hemisphere) and are tilted at the optimal angle capture more sunlight, improving the TSRF.
- Shading: Trees, buildings, and other obstacles that block sunlight lower the TSRF value. Minimizing shading is critical to maximize solar energy generation.
- Atmospheric Conditions: Weather patterns, including clouds, rain, and snow, can reduce the sunlight received by the panels, impacting TSRF.
- Panel Efficiency: The type and efficiency of the solar panels themselves also influence the overall TSRF, as more efficient panels will convert more sunlight into electricity.
TSRF Solar Example: How It Works in Practice
- Imagine you are planning to install solar panels on a roof in a suburban area. The first step is to calculate the TSRF for that location, which includes measuring the roof’s tilt, orientation, shading, and surrounding environmental factors.
- For instance, a site with minimal shading, optimal tilt, and a southern-facing orientation may have a TSRF of 90-100%, indicating it has a high solar potential. On the other hand, if there are significant trees casting shadows over the roof, the TSRF could drop to 60%, meaning the energy generation will be lower.
How to Improve TSRF for Your Solar Installation
If your site’s TSRF is lower than expected, there are several steps you can take to improve it:
- Trim or remove trees that block sunlight.
- Adjust the tilt of your panels to optimize the angle of sunlight exposure.
- Reposition panels to ensure they face the optimal direction (usually south in the Northern Hemisphere).
- Use advanced solar technologies like PERC panels to boost energy production, even with less-than-ideal conditions.
Canonical
This article explains TSRF Solar (Total Solar Resource Fraction) and its role in determining the solar energy potential of a location. It covers factors like shading, orientation, tilt, and panel efficiency that impact TSRF. Understanding TSRF is essential for optimizing solar installations and maximizing energy production.
Want to learn more about solar energy? Explore our other informative articles on solar solutions and maximize your energy potential!
What Does TSRF Mean in Solar?
TSRF (Total Solar Resource Fraction) is a measurement that evaluates the solar energy potential of a specific location. It accounts for solar access, the tilt of the panels, and the orientation to give a percentage value, with 100% being the ideal solar resource for the site.
What Is a Good TSRF for Solar?
A good TSRF for solar installations is typically 75% or higher. For on-site assessments, a TSRF of 75% or above is considered adequate to qualify for solar energy incentives and installation. The higher the TSRF, the more sunlight the site receives, increasing its solar energy potential.
How Do You Calculate TSRF?
To calculate TSRF, compare the Shaded Irradiance to the Optimal POA Irradiance. For example, in HelioScope, if the shaded irradiance is 1910.4 kWh/m² and the optimal irradiance is 2165.1 kWh/m², the TSRF equals 88.2%. This can also be calculated by multiplying the Tilt and Orientation Factor (TOF) by the Solar Access %, which gives the same value.
What Is the TSRF Rating?
The TSRF rating is the final percentage that reflects how much solar energy a location can effectively capture. It’s calculated by multiplying the Solar Access percentage by the Tilt and Orientation Factor (TOF), providing a clearer picture of the available solar energy and its suitability for solar panel installations.
How Can TSRF Be Improved for Solar Panels?
To improve TSRF, you can minimize shading, optimize the tilt of the panels, and adjust the orientation. Removing obstacles like trees or buildings that block sunlight, and ensuring panels face the ideal direction, can significantly enhance the TSRF value.
Why Is TSRF Important for Solar System Design?
TSRF is vital for solar system design because it helps predict the amount of sunlight a site will capture, which directly affects the energy output. By understanding TSRF, solar professionals can make more accurate predictions, choose the best location for panels, and optimize system performance.
What Is the Ideal TSRF for Solar Installations?
An ideal TSRF for solar installations typically falls between 80% to 100%, meaning the site captures most of the sunlight available. Sites with TSRF values below 75% may experience reduced solar energy production due to factors like shading or less-than-optimal panel positioning.
How Does Geographical Location Affect TSRF?
The geographical location of a site plays a key role in determining TSRF. Locations near the equator receive more sunlight throughout the year, which leads to higher TSRF values, while regions near the poles receive less sunlight, resulting in lower TSRF values.
What Is the Relationship Between TSRF and Solar Access?
Solar access refers to the amount of sunlight a site can receive, and it directly impacts the TSRF. A higher solar access percentage results in a higher TSRF value, indicating better conditions for solar power generation. Poor solar access due to shading or obstructions lowers the TSRF.
Can TSRF Be Used for Both Residential and Commercial Solar?
Yes, TSRF is used for both residential and commercial solar installations. In both cases, TSRF helps assess how much solar energy can be generated based on location-specific factors like shading, panel tilt, and orientation, ensuring an optimized and efficient solar system.
Please Write Your Comments