Power and Energy: Step-by-Step Complete Guide for You! Understanding Kilowatts, Solar Systems, and More
Updated: 16 Jan 2025
111
What is Power and Energy?
Power and energy are terms we all encounter in daily life, especially when dealing with electricity and solar energy. But let me tell you from experience many people confuse these two, even though they are distinctly different. So, let’s clarify:
- Power is the rate at which energy is used or transferred. It’s the speed at which energy flows through your devices. Think of it as the strength or intensity of energy being consumed at a given moment.
- Energy, on the other hand, is the total amount of power used over time. It’s what gets consumed or stored, measured over a period.
Understanding the difference is absolutely crucial whether you’re managing your home’s electricity usage or evaluating a solar energy system. The more you understand, the better decisions you can make when it comes to reducing energy waste and saving on costs.
Why Understanding the Difference is Important
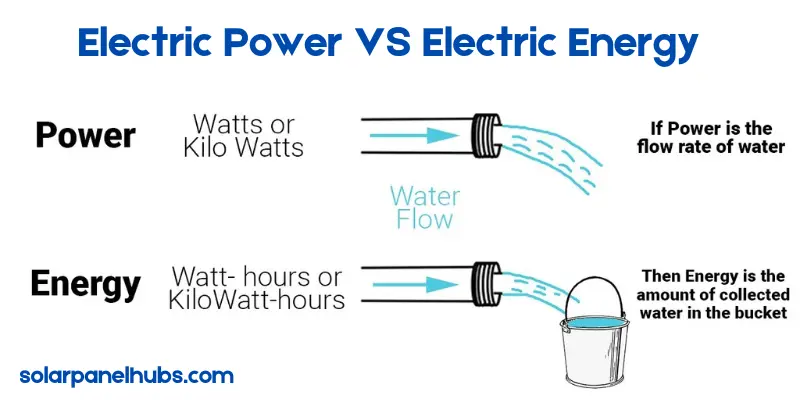
Let me explain why this matters. When you check your electricity bill, you’ll see it in kilowatt-hours (kWh), not just kilowatts (kW). Here’s the difference:
- kWh tells you how much total energy you’ve used over time.
- kW just shows how much power is being used at any given moment.
From years of experience, I can tell you knowing this difference helps you track your energy usage better and gives you the tools to use less energy, whether you’re using solar or regular power from the grid.
Ever wondered why your electricity bill uses terms like ‘kWh’ instead of just ‘kW’? It’s because these two terms, power and energy, are not the same, and understanding the difference can help you make smarter choices with your energy use. Let’s break it down!
Understanding Power
1. Definition of Power
Power is simply the rate at which energy is used or transferred. Imagine it like the speed at which energy is flowing. The faster the flow, the more power is being used.
Unit of Power:
Power is measured in Watts (W), Kilowatts (kW), and Megawatts (MW). To give you an idea:
- 1 Watt (W) = The amount of power used by a small device.
- 1 Kilowatt (kW) = 1,000 Watts. This is a common unit for appliances.
- 1 Megawatt (MW) = 1,000,000 Watts. This is used for large power plants or industrial systems.
2. Real-life Example:
A simple example: A 60W light bulb uses 60 watts of power. This means it’s using 60 watts of energy every second it’s on. Power tells you how quickly energy is being consumed. Think of it as how fast your light bulb is “eating” electricity.
2. Power in Solar Systems
When we talk about solar systems, the power rating tells us how much energy a system can produce in a given time. For example, a 5 kW solar system can generate 5 kilowatts of power in perfect conditions. But in real life, this number fluctuates based on weather, panel cleanliness, and other factors.
From my experience working with solar installations, I’ve seen many people confused about this—thinking their system will always produce at its peak rating. The reality is, it rarely does, because power production depends on the sun’s intensity and the system’s efficiency.
“This research and these insights come from years of industry experience and feedback from various labs and installations, including studies conducted by institutions like the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the U.S., which focuses on solar energy technologies.”
Understanding Energy
1. Definition of Energy
Energy is the capacity to do work or produce heat. Simply put, it’s the “fuel” that powers everything, from light bulbs to machines.
Unit of Energy:
Energy is measured in Joules, Watt-hours (Wh), and Kilowatt-hours (kWh). To break it down:
1 Joule (J) is the basic unit of energy.
1 Watt-hour (Wh) is the amount of energy used by a device consuming 1 watt of power for 1 hour.
1 Kilowatt-hour (kWh) is 1,000 Watts-hours and is commonly used for electricity billing.
2. Real-life Example:
A 60W light bulb uses 60W of power. But if it runs for 5 hours, it will consume 300Wh of energy (60W × 5 hours = 300Wh). This shows the total energy the bulb uses over that time.
3. Energy in Solar Systems
In solar systems, energy is measured over time. For example, if your solar system produces 10 kWh of energy in one day, it means your system generates 10 kilowatt-hours of energy from sunlight. This is what you’d use to power your home or store in a battery.
From my experience in solar installations, I’ve worked with systems that can generate anywhere between 5-30 kWh per day, depending on panel size, location, and weather.
Key Differences Between Power and Energy
Power vs Energy in Simple Terms
The main difference between power and energy is simple:
- Power is the rate at which energy is used. It’s how fast energy is consumed at any given moment.
- Energy is the total amount used over time. It’s the “total fuel” used, not just how fast it’s being used.
Key Characteristics of Power
- Instantaneous Usage: Power tells you how quickly energy is being used or transferred at a specific moment. For example, a microwave uses a certain amount of power when it’s on.
- Measured in Watts: Power is typically measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). For example, a microwave that runs at 1000W uses 1000 watts of power when it’s on.
Key Characteristics of Energy
- Cumulative Usage Over Time: Energy is the total amount used over a period. It’s a measure of the total work done or heat produced.
- Measured in Kilowatt-hours (kWh): Energy is usually measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This is what you see on your electricity bill.
Examples of Power and Energy in Daily Life
- Power Example: A microwave running at 1000W means it uses 1000 watts of power every second it’s on. This tells you how fast the microwave is consuming energy.
- Energy Example: If that same microwave runs for 30 minutes (0.5 hours), it will consume 500Wh (0.5kWh) of energy. This tells you how much energy the microwave used over that time.
The Relationship Between Power and Energy
1. How Power and Energy Work Together
Power and energy are closely related. Here’s how they work together:
- Power is how quickly energy is used or transferred at a specific moment.
- Energy is the total amount of power used over a period of time.
The formula that connects power and energy is:
Energy = Power × Time
(E = P × t)
This means the total energy used (E) is equal to the power (P) multiplied by the time (t) it is used.
2. Why This Matters in Real Life
Understanding the relationship between power and energy helps us calculate how much energy appliances or solar systems use. It’s the key to understanding your energy consumption and optimizing it.
For example, if you have a 3 kW solar panel system, it can produce 3 kW of power every hour under perfect conditions. To calculate the total energy produced over time:
- Energy produced in 5 hours = Power × Time
- Energy = 3 kW × 5 hours = 15 kWh
This means, that in 5 hours, your 3 kW solar panel system will produce 15 kWh of energy.
This calculation helps you understand how much energy your system generates over time, which is important for both estimating electricity usage and maximizing solar energy efficiency.
Examples of Power and Energy in Solar Systems
Solar Panel Power Ratings
Solar panels are rated based on the amount of power they can produce under perfect conditions. This is usually measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). For example, you might have a solar panel that is rated at 300W or 400W.
- A 300W panel produces 300 watts of power in full sunlight.
- A 400W panel produces 400 watts of power in the same conditions.
The more power a panel can produce, the higher its watt rating. However, keep in mind that actual power production can vary due to weather conditions and other factors.
Energy Production from Solar Systems
While power tells you how much energy is used at a given moment, the energy produced by a solar system is measured over time. This is where kilowatt-hours (kWh) come in.
- A solar system’s energy production depends on how long the panels are exposed to sunlight. For example, a 5 kW solar system can produce 5 kW of power in one hour under optimal conditions.
Example
A typical 5 kW solar system can produce about 20 kWh per day, assuming around 4-5 hours of good sunlight. This is because:
- 5 kW × 4 hours = 20 kWh (energy produced over 4 hours of peak sunlight).
This energy can be used to power your home or be stored in a battery for later use.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between power and energy can be very beneficial for you.
- Power is what your devices are using at a specific moment, measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
- Energy, on the other hand, is what your device consumes over time, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
By understanding this difference, you can manage your electricity usage more effectively, especially if you are using a solar energy system. The next time you think about your electricity bill or solar system, remember: that power refers to how quickly energy is being used, while energy refers to the total amount you are consuming. This understanding will help you have better control over your energy consumption.
Did this clear up the confusion between power and energy for you? Feel free to leave a comment below and share your thoughts I’d love to hear how this information helped you! If you’re interested in learning more about solar energy and related topics, visit solarpanelhubs.com for more insightful articles and tips.
What’s the difference between a kilowatt (kW) and a kilowatt-hour (kWh)?
- Kilowatt (kW) is a unit of power that measures the rate at which energy is used or produced at a given moment. For example, a 1 kW appliance uses 1,000 watts of power continuously.
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of energy, measuring how much power is used over time. For example, a 1 kW appliance running for 1 hour will consume 1 kWh of energy.
How does understanding power and energy help with my electricity bill?
By understanding power and energy, you can better manage your usage and reduce waste. Your electricity bill is based on the total energy (kWh) you use. Knowing the power rating of your appliances (in kW) and how long they run will help you estimate and control your energy consumption, thus saving money.
Can you give an example of how much energy a solar system generates per day?
For example, a 5 kW solar system in good conditions can generate around 20 kWh per day (if it gets about 4-5 hours of good sunlight). The energy generated depends on factors like sunlight hours and the efficiency of the system.
Why is power important in solar systems?
Power is crucial in solar systems because it determines the maximum rate at which energy can be produced. The power rating of a solar panel or system tells you how much electricity it can generate at peak performance. This helps in sizing the system to meet energy needs and understanding how much power your solar setup can provide at any given time.
What is the relationship between power and energy?
Power is the rate at which energy is used or transferred. It is calculated by dividing energy by the time taken to use that energy. Power is measured in watts (W), where 1 watt equals 1 joule per second.
Is electricity a power or energy?
Electricity is the flow of electrical power or charge. It is both a form of energy and a way energy is transmitted, making it essential for powering devices.
What is the difference between current power and energy?
Current refers to the flow of electricity, and power is the amount of energy used over time. Power is calculated by multiplying voltage by current, and energy is the total power used over a period of time.
Is light a form of energy?
Yes, light is a type of radiant energy, which is one of the many forms of energy we encounter in daily life.
What is the SI unit of energy?
The SI unit of energy is the joule (J), which represents the energy required to move an object using a force of one Newton over a distance of one meter.
What are the similarities between power and energy?
Both power and energy are scalar quantities (they only have magnitude, not direction). They can both be transferred from one object to another, such as when electrical energy moves from the power grid to a light bulb.
How do you calculate power?
Power is calculated as the rate at which energy is transferred, using the formula: P = W/t, where P is power, W is work or energy, and t is time. Power is measured in watts (W).
What are the 7 main energy types?
- The 7 main types of energy are:
- Mechanical
- Electrical
- Chemical
- Radiant (light)
- Thermal (heat)
- Sound
- Nuclear These forms of energy are often transformed into each other in everyday processes.
What is the formula for energy?
The famous formula developed by Albert Einstein is E = mc², where E is energy, m is mass, and c is the speed of light. This shows how energy and mass are related.
Please Write Your Comments