Solar Grid for Home – Benefits, Setup, Cost, Challennges, Future
Updated: 13 Dec 2024
98
Introduction
Solar energy has become a popular choice for homeowners looking to reduce their electricity bills and make a positive environmental impact. A solar grid for home harnesses the power of the sun, providing clean and renewable energy. As more people seek sustainable solutions, the demand for solar grids has skyrocketed, making it easier and more affordable to switch to solar energy.
Are you thinking about switching to a solar grid for your home but unsure if it’s the right choice? What factors are holding you back from making the change? Let’s explore how solar energy can benefit you and your family while protecting the planet.
What is a Solar Grid for Home?
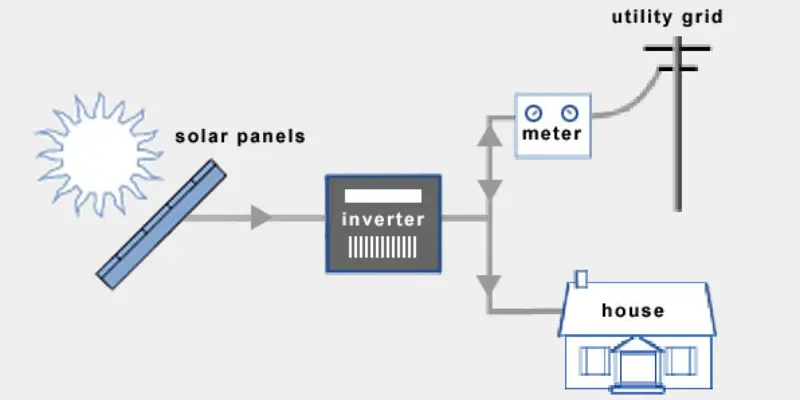
A solar grid for home is a system where solar panels are installed on your roof to generate electricity. These panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power your home. In many cases, the system is connected to the main electrical grid, allowing you to use both solar energy and grid power when needed.
So, how does it work? Solar panels capture sunlight and turn it into direct current (DC) electricity. An inverter then converts this DC into alternating current (AC), which your home uses. If the panels produce more energy than you need, the extra electricity is sent back to the grid. This can help lower your electricity bills or even earn you credits from your utility company.
- Example: think of having solar panels on your roof that power your lights, TV, and appliances—while any extra energy is shared with the grid to benefit others.
Benefits of a Solar Grid for Your Home
Environmental Benefits
- Using a solar grid for your home significantly reduces your carbon footprint. Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that doesn’t produce harmful greenhouse gases like traditional fossil fuels. By switching to solar, you help lower global warming potential and contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment.
- Example: A typical home can reduce CO2 emissions by over 100 tons during the lifetime of a solar system.
Financial Benefits
- Switching to a solar grid for your home can lower your monthly energy bills. By generating your own electricity, you reduce the amount of energy you need to buy from the grid. Additionally, many governments offer tax credits, rebates, and incentives to make solar more affordable.
- Example: Homeowners can save thousands over the years on electricity costs, and some even earn back the installation cost through savings.
Energy Independence
- A solar grid allows homeowners to become less dependent on the electrical grid, offering more control over their energy use. During power outages or periods of high demand, homes with solar power systems (especially with battery storage) can continue to function normally.
- Example: Imagine a power blackout where your solar-powered home remains lit, with appliances running, while others are left without power.
Key Components of a Home Solar Grid System
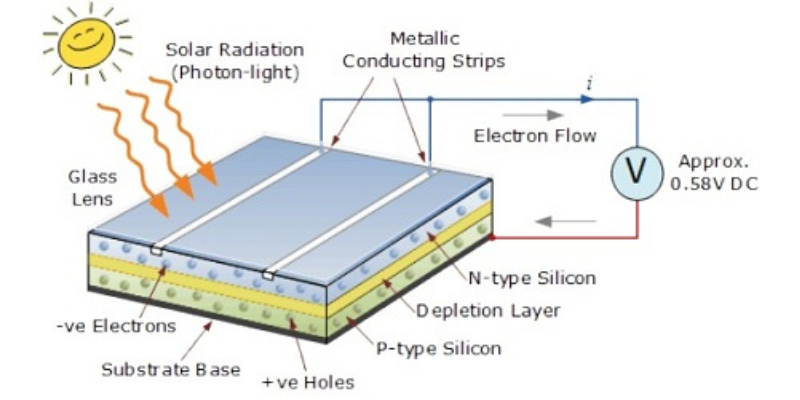
Solar Panels
- Solar panels are the core of a solar grid system. There are two main types: monocrystalline and polycrystalline. Monocrystalline panels are more efficient and last longer, while polycrystalline panels are more affordable but slightly less efficient.
Inverter
- The inverter is crucial as it converts the DC (direct current) power produced by solar panels into AC (alternating current) power, which is what home appliances use.
Battery Storage (Optional)
- Battery storage, like the Tesla Powerwall, allows homeowners to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during cloudy periods, ensuring a consistent power supply.
Connection to the Grid
- Homes can connect their solar grid to the main electrical grid. This allows them to either feed excess energy back into the grid or draw power from it when solar generation is insufficient, often through net metering.
How to Set Up a Solar Grid for Your Home
Step 1: Assessing Your Energy Needs
- Start by reviewing your home’s energy consumption. Look at your monthly electricity bills to determine how much power you use. This helps you choose the right size for your solar system, ensuring you generate enough energy for your home.
Step 2: Choosing the Right Solar Panels
- Consider factors such as panel efficiency, cost, and available space when selecting solar panels. Monocrystalline panels offer higher efficiency but come at a higher cost, while polycrystalline panels are more affordable but less efficient. Choose based on your needs and budget.
Step 3: Installation Process
- The installation process involves several steps: obtaining necessary permits, hiring contractors, and installing the system. The time from consultation to installation can vary but usually takes a few weeks. The contractor will guide you through the entire process.
Step 4: Maintenance and Monitoring
- To ensure your solar grid operates efficiently, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential. There are various tools and apps available that can help you track your solar system’s performance, alerting you to any issues. Keep an eye on your system to ensure it’s always producing energy efficiently.
Cost of Installing a Solar Grid for Home
Initial Cost
- The average cost of installing a solar grid for a home depends on the size of the system, the type of panels used, and the complexity of installation. Costs can range from $10,000 to $25,000 for an average-sized home. Factors like roof condition, panel efficiency, and location can influence the price.
Long-term Savings
- Although the initial investment can be high, solar energy systems pay for themselves over time. Homeowners can save on electricity bills, and with the right system, they may even generate surplus energy that can be sold back to the grid. Over 20-25 years, a solar system can save tens of thousands of dollars.
Government Incentives and Rebates
- Many regions offer financial assistance to make solar grid installation more affordable. This includes federal tax credits, state rebates, and local programs that help reduce the upfront costs of installation. Always check for available incentives in your area to maximize savings.
Tip: Visit government websites or trusted solar providers to find current rebates and tax credits available in your area.
Challenges of Installing a Solar Grid for Home
Upfront Investment
- The initial cost of installing a solar grid can be a significant barrier for many homeowners. While the system pays for itself over time through energy savings, the upfront investment can still be daunting. Fortunately, financing options and incentives can help reduce the financial burden.
Space Limitations
- Not every home has enough roof space to accommodate a full solar panel system. In such cases, homeowners can consider alternative solutions like ground-mounted solar panels or smaller, more efficient panels. Consulting a solar provider can help determine the best solution for limited space.
Weather Dependency
- Solar systems may not produce as much energy on cloudy days or during bad weather, but modern solar panels are designed to work efficiently even in low-light conditions. Battery storage can help store excess energy for use during these times, ensuring a reliable power supply throughout the year.
Future of Solar Grid for Home
Advancements in Solar Technology
- Solar technology is rapidly advancing, making solar panels more efficient, affordable, and easier to integrate into homes. Innovations like solar tiles and transparent solar windows are opening up new possibilities for homeowners, blending energy production seamlessly with modern home design. These advancements promise not only better energy efficiency but also enhanced aesthetic appeal.
Global Trends and Adoption
- The global shift toward renewable energy is accelerating the adoption of solar grids in homes. Countries like Germany and Australia are leading the way with widespread solar adoption, incentivizing homeowners to make the switch. As more governments and industries push for clean energy, we can expect solar grids to become an even more viable and widespread solution for homeowners worldwide.
Conclusion
Switching to a solar grid for the home offers a powerful combination of financial savings, environmental benefits, and energy independence. By harnessing solar energy, you can reduce your electricity bills, contribute to a cleaner planet, and gain more control over your energy consumption.
Take the first step towards a more sustainable future by consulting a local solar provider. Explore available solar green energy solutions and learn about incentives in your area to make the transition more affordable. Start with a free consultation to assess how a solar grid can benefit your home today!
How long does it take for a solar grid system to pay for itself?
The payback period for a solar grid for home typically ranges from 6 to 10 years, depending on factors like energy savings, system size, and local electricity rates. Over time, the system can provide significant savings, especially with incentives and rebates.
Can I install a solar grid if my home doesn’t get a lot of sunlight?
Yes, solar panels can still work in less sunny regions, though their efficiency may be reduced. Even in cloudy or partially sunny areas, modern solar technology is designed to capture diffuse sunlight and generate power.
Are solar grids expensive to maintain?
Solar grids are relatively low-maintenance. The primary cost is cleaning panels and occasional system checks. Most systems come with long warranties, and the maintenance cost is minimal compared to the long-term savings from reduced energy bills.
Can I use solar power at night or during cloudy days?
Yes, you can use solar power at night or on cloudy days if you have a battery storage system. Excess energy generated during the day is stored in batteries (like the Tesla Powerwall) for later use when the sun isn’t shining.
What happens if I generate more solar power than I need?
Excess energy can be fed back into the electrical grid, and you may receive credits for it through a process called net metering. This helps reduce your energy bills even further.
Do I need to replace my solar panels after a few years?
No, solar panels typically last 25-30 years with minimal degradation. After this time, they may still produce power, though at a reduced efficiency. Regular maintenance can help extend the lifespan of the system.
Is it possible to install solar grids on a flat roof?
Yes, solar panels can be installed on both sloped and flat roofs. For flat roofs, mounting systems are used to position the panels at an optimal angle to maximize sunlight absorption.
How do I choose the best solar panels for my home?
Consider factors such as panel efficiency, cost, available roof space, and warranty. Monocrystalline panels tend to be more efficient but also more expensive, while polycrystalline panels are cheaper but less efficient. A professional solar consultant can help you make the best choice based on your needs.
Please Write Your Comments